The Graphics module provides a JavaScript API for creating shapes in a variety of formats across a browser test baseline. Based on device and browser capabilities, Graphics leverages SVG, HTML Canvas and VML to render its graphical elements.
The Graphics module provides a JavaScript API for creating shapes in a variety of formats across a browser test baseline. Based on device and browser capabilities, Graphics leverages SVG, HTML Canvas and VML to render its graphical elements.
The Graphics module features a Graphic class that allows you to easily create and manage shapes. Currently, a Graphic instance can be used to create predifined shapes and free-form polygons with fill and stroke properties.
Getting Started
To include the source files for Graphics and its dependencies, first load the YUI seed file if you haven't already loaded it.
<script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/3.8.0/build/yui/yui-min.js"></script>
Next, create a new YUI instance for your application and populate it with the
modules you need by specifying them as arguments to the YUI().use() method.
YUI will automatically load any dependencies required by the modules you
specify.
<script>
// Create a new YUI instance and populate it with the required modules.
YUI().use('graphics', function (Y) {
// Graphics is available and ready for use. Add implementation
// code here.
});
</script>
For more information on creating YUI instances and on the
use() method, see the
documentation for the YUI Global Object.
Using the Graphics module
The Graphic class acts a factory and container for shapes. You need at least one Graphic instance to create shapes for your application.
Instantiating A Graphic instance
All you need to instantiate a Graphic instance is an HTML element in which to render. Alternatively, you can attach your instance to the body of your page.
CSS
#mygraphiccontainer {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
}
HTML
<div id="mygraphiccontainer"></div>
JavaScript
// Instantiate a graphic instance
var mygraphic = new Y.Graphic({
render: "#mygraphiccontainer"
});
By default, Graphic will size to its parent container. The API also provides the option of explicitly setting its width and height attributes. Additionally, the Graphic class provides an autoSize attribute. When set to true, the Graphic instance will expand to fit its contents.
Creating shapes
Shapes are created using the addShape method. The addShape method takes a config parameter that defines the shape and its properties. When creating a shape, the shape is determined by the type
attribute. The Graphics module includes four pre-defined shapes. They can be created by passing a String reference.
| key | shape |
|---|---|
| circle | Y.Circle |
| ellipse | Y.Ellipse |
| rect | Y.Rect |
| path | Y.Path |
Alternatively, you can create your own custom class and pass it directly through the type attribute.
The below code would create a 300x200 rectangle with a blue fill and a red border.
var mygraphic = new Y.Graphic({render:"#mygraphiccontainer"}),
myrect = mygraphic.addShape({
type: "rect",
width: 300,
height: 200,
fill: {
color: "#0000ff"
},
stroke: {
weight: 2,
color: "#ff0000"
},
x: 50,
y: 100
});
This code would create an instance of a custom shape that you have created.
var mygraphic = new Y.Graphic({render:"#mygraphiccontainer"}),
myrect = mygraphic.addShape({
type: Y.MyCustomShape,
width: 300,
height: 200,
fill: {
color: "#0000ff"
},
stroke: {
weight: 2,
color: "#ff0000"
},
x: 50,
y: 100
});
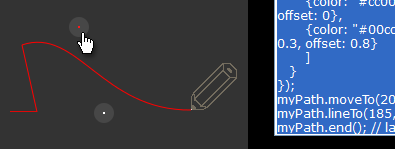
Path Drawing Tool
Try this simple tool that helps you by generating code while you interactively draw graphic paths.
As you drag the pencil icon, corresponding graphics code is auto-generated. This code can be copied and pasted into a graphics instance to reproduce the paths you created with the pencil.
The violin example was created with this tool.
Working with the Graphic Class
The Graphics module uses different technologies based on browser capabilities. The Graphics module normalizes these different technologies with a consistent API. Ideally, you should not
have to interact directly with the underlying technologies or their corresponding HTML elements. Both the Graphic and Shape classes provide APIs for sizing, positioning and customization.
Graphic Attributes
The Graphic class exposes the following attributes.
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
String |
Unique identifier for the Graphic instance. If not explicity set, one will be generated. |
shapes |
Object |
Key value pairs containing all shape instances contained in the Graphic instance. |
contentBounds |
Object |
Object containing size and coordinate data for the content of a Graphic in relation to the coordinate space of the Graphic instance. The following values are included: top, right, bottom, left, width and height. |
node |
HTMLElement |
Outermost HTMLElement of the Graphic instance. (read-only) |
width |
Number |
The width of the Graphic instance. |
height |
Number |
The height of the Graphic instance. |
autoSize |
boolean |
Determines the sizing of the graphic. See the API Docs for possible values and associated behaviors. |
preserveAspectRatio |
String |
Determines how content is sized when autoSize is set to sizeContentToGraphic. See the API Docs for possible values. |
resizeDown |
boolean |
The contentBounds will resize to greater values but not to smaller values. (for performance) When resizing the contentBounds down is desirable, set the resizeDown value to true. The default value is false. |
x |
Number |
Indicates the x-coordinate for the instance. |
y |
Number |
Indicates the y-coordinate for the instance. |
autoDraw |
boolean |
Indicates whether or not the instance will automatically redraw after a change is made to a shape. When performing multiple operations, such adding many shapes, autoDraw can be set to false. Calling _redraw will force a redraw when autoDraw is false. |
visible |
boolean |
Toggles visibility for a Graphic instance. |
Graphic Methods
The Graphic class also has the following public methods.
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
| getXY | Returns an array containing the current position of the graphic instance in page coordinates. |
| addShape | Generates and returns a shape instance by type. |
| removeShape | Removes a shape instance from from the graphic instance. |
| removeAllShapes | Removes all shape instances |
| destroy | Destroys the graphic instance and all its children. |
| getShapeById | Returns a shape instance based on an id. |
| batch | Allows for creating multiple shapes in order to batch appending and redraw operations. |
Working with Shapes
Shape Attributes
Each shape shares a common set of attributes. Attributes shared across all shapes are listed below:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
String |
Unique identifier for the Shape instance. If not explicity set, one will be generated. |
node |
HTMLElement |
HTMLElement of the Shape instance. (read-only) |
data |
String |
Represents an SVG Path string. This will be parsed and added to shape's API to represent the SVG data across all implementations. Note that when using VML or SVG implementations, part of this content will be added to the DOM using respective VML/SVG attributes. If your content comes from an untrusted source, you will need to ensure that no malicious code is included in that content. |
x |
Number |
The x-coordinate of the shape. |
y |
Number |
The y-coordinate of the shape. |
width |
Number |
The width of the Shape instance. |
height |
Number |
The height of the Shape instance. |
visible |
boolean |
Toggles visibility for a Shape instance. |
fill |
Object |
Contains information about the fill of the shape. |
| stroke | Object |
Contains information about the stroke of the shape. |
transformOrigin |
Array |
The x and y values for the transformOrigin of a transform. |
transform |
String |
A string containing, in order, transform operations applied to the shape instance. The transform string can contain the following values:
transform attribute to instantiate a recangle with a rotation of 45 degrees.
var myRect = new Y.Rect({
type:"rect",
width: 50,
height: 40,
transform: "rotate(45)"
};
The code below would apply translate and rotate to an existing shape.
myRect.set("transform", "translate(40, 50) rotate(45)");
|
Shape Methods
Shapes can also be manipulated by the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
addClass |
Adds a class to the underlying HTMLElement. |
removeClass |
Removes a class to the underlying HTMLElement. |
getXY |
Gets the current position of the shape in page coordinates. Returns an array, [x, y,], with the coordinates. |
setXY |
Sets the current position of the shape in page coordinates. Accepts an array, [x, y], with the coordinates. |
get |
Returns the value of a given attribute. |
set |
Sets the value of an attribute. |
rotate |
Rotates the shape clockwise around it transformOrigin. |
translate |
Specifies a 2d translation. |
translateX |
Translates the shape along the x-axis. |
translateY |
Translates the shape along the y-axis. |
skew |
Skews the shape around the x-axis and y-axis. |
skewX |
Skews the shape around the x-axis. |
skewY |
Skews the shape around the y-axis. |
scale |
Specifies a 2d scaling operation. |
Drawing Methods
Unlike the other included shapes, the Path class is not pre-defined. Setting the size, fill and/or stroke of a pre-defined shape will render the shape. This is not true with the Path. To render
a Path instance, its drawing methods need to be leveraged. These drawing methods can also be leveraged when creating custom shapes. Available drawing methods include:
- moveTo
- Moves to a coordinate point without drawing a line.
- lineTo
- Draws a line segment from the current point to the specified point.
- curveTo
- Draws a curve based on a start point, end point and two control points.
- quadraticCurveTo
- Draws a quadratic curve based on a start point, end point and two control points.
- end
- Ends a drawing operation. The path or custom shape will draw after end is called.
- clear
- Clears all contents of a path or custom shape.
Strokes and Fills
All Shape instances contain stroke and fill attributes. They are used to define the colors for a Shape.
Defining a Stroke
The stroke attribute has six properties.
- color
- The color of the stroke.
- weight
- Number that indicates the width of the stroke.
- opacity
- Number between 0 and 1 that indicates the opacity of the stroke. The default value is 1.
- dashstyle Indicates whether to draw a dashed stroke. When set to "none", a solid stroke is drawn. When set to an array, the first index indicates the length of the dash. The second index indicates the length of gap.
- linecap
- Specifies the linecap for the stroke. The following values can be specified:
- butt (default)
- Specifies a butt linecap.
- square
- Specifies a sqare linecap.
- round
- Specifies a round linecap.
- linejoin
- Specifies a linejoin for the stroke. The following values can be specified:
- round (default)
- Specifies that the linejoin will be round.
- bevel
- Specifies a bevel for the linejoin.
- miter limit
- An integer specifying the miter limit of a miter linejoin. If you want to specify a linejoin of miter, you simply specify the limit as opposed to having separate miter and miter limit values.
The code below would set a 2 pixel solid red stroke on myshape.
myshape.set("stroke", {
color: "#ff0000",
weight: 2
});
The dashstyle property can be used to create a dashed stroke on a shape.
myshape.set("stroke", {
color: "#ff0000",
weight: 2,
dashstyle: [3, 2]
});
Defining a Fill
The fill attribute has the following properties.
- color
- The color of the fill.
- opacity
- Number between 0 and 1 that indicates the opacity of the fill. The default value is 1.
- type
- Type of fill.
- solid
- Solid single color fill. (default)
- linear
- Linear gradient fill.
- radial
- Radial gradient fill.
If a linear or radial is specified as the fill type. The following additional property is used:
- stops
- An array of objects containing the following properties:
- color
- The color of the stop.
- opacity
- Number between 0 and 1 that indicates the opacity of the stop. The default value is 1. Note: No effect for IE <= 8
- offset
- Number between 0 and 1 indicating where the color stop is positioned.
- rotation
- Linear gradients flow left to right by default. The rotation property allows you to change the flow by rotation. (e.g. A rotation of 180 would make the gradient pain from right to left.)
- r
- Radius of the gradient circle.
- fx
- Focal point x-coordinate of the gradient.
- fy
- Focal point y-coordinate of the gradient.
- cx
- The x-coordinate of the center of the gradient circle. Determines where the color stop begins. The default value 0.5.
Note: This property currently has no effect on Android or IE 6 - 8.
- cy
- The y-coordinate of the center of the gradient circle. Determines where the color stop begins. The default value 0.5.
Note: This property currently has no effect on Android or IE 6 - 8.
Linear gradients also have the following property:
Radial gradients have the following additional properties:
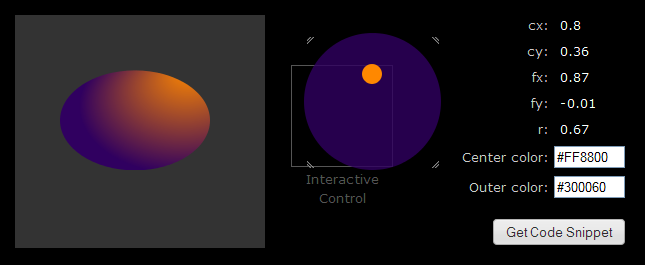
Radial Gradient Tool
Try this simple tool that helps
you interactively preview radial gradient fills.
Try It
Avoid the trial and error, quickly get just the look you want. As you drag and resize different parts of the control, you preview the radial gradient fill and see its property values update. Click the "Get Code Snippet" button for code you can paste into a Graphics instance to reproduce the same gradient.
Known Issues
-
Gradients need more need more normalization across technologies. Certain gradient types have limitations on different browsers.
- Radial gradients contain the properties
cxandcy. These properties currently have no impact on Android or IE 6 - 8. - After being initially set, gradients cannot be updated in IE 6 - 8.
- Radial gradients contain the properties
-
Path element currently lacks the ability to have interactivity in Android.